The IT Landscape and Certifications
- Information Technology (IT): Encompasses the relationship between hardware, software, networks, and technical support.
- IT Essentials: A course that provides foundational knowledge on PC hardware and software.
- CompTIA A+: An industry-standard certification for computer service technicians.
- European Certification of Informatics Professionals (EUCIP): Another IT certification program.
Introduction to Personal Computers
- Personal Computers (PCs): Programmable devices for general-purpose computing.
- Form Factors: Different PC sizes and configurations (desktop, tower, mini-tower, laptop, etc.).
- Desktop vs. Laptop: Desktops offer more upgradeability and power, while laptops prioritize portability.
Understanding Hardware Components
- Case: Protects internal components and provides airflow for cooling.
- Materials: Typically steel or plastic.
- Form Factor Compatibility: Cases are designed for specific motherboard sizes (ATX, microATX, etc.).
- Expansion Slots: Allow for installing additional components like graphics cards.
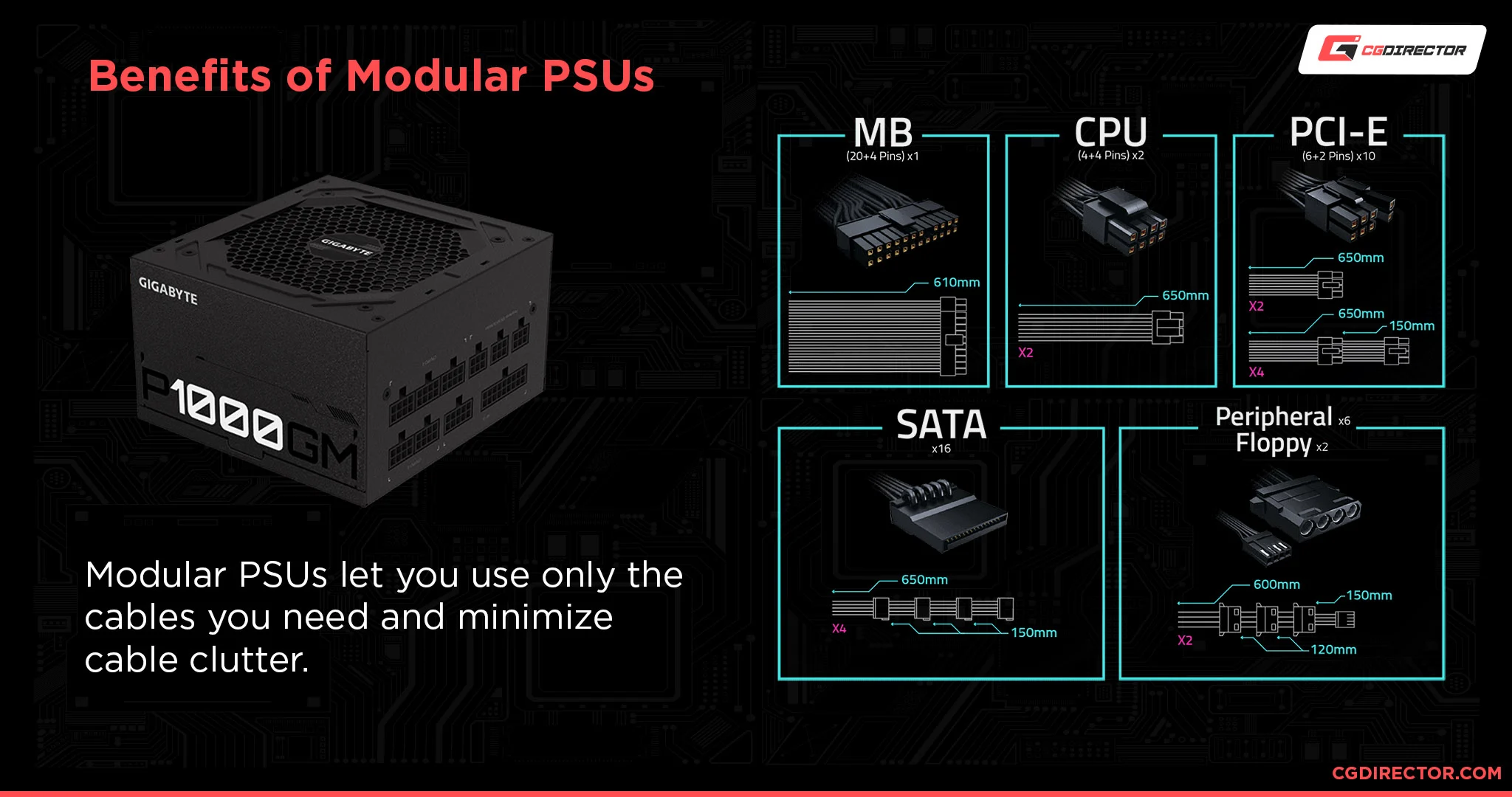
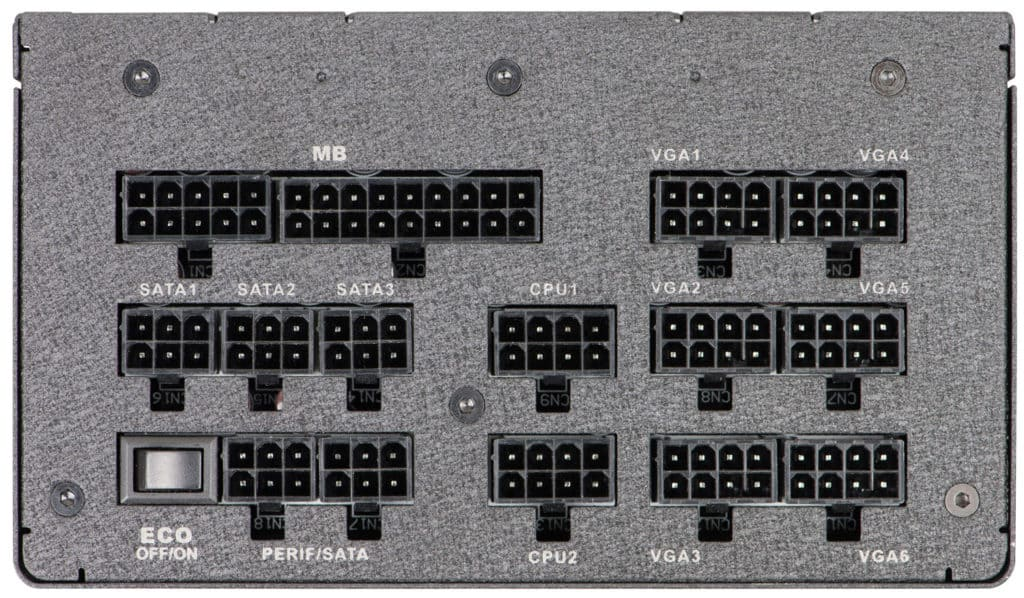
- Power Supply Unit (PSU) Mounting: PSU provides power to all components and mounts in a designated location.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts AC power from the wall outlet to DC voltages usable by the computer.
- Wattage Rating: Indicates the amount of power the PSU can deliver (important for high-performance systems).
- Has 3.3v, 5v & 12v outputs
- Form Factor Compatibility: PSUs come in different sizes to fit specific cases: common types are AT (advanced technology), ATX (AT extended) & ATX12v (most common), EPS12V (high end desktop & servers)
- Fan Cooling: PSUs use fans to expel heat generated during power conversion.
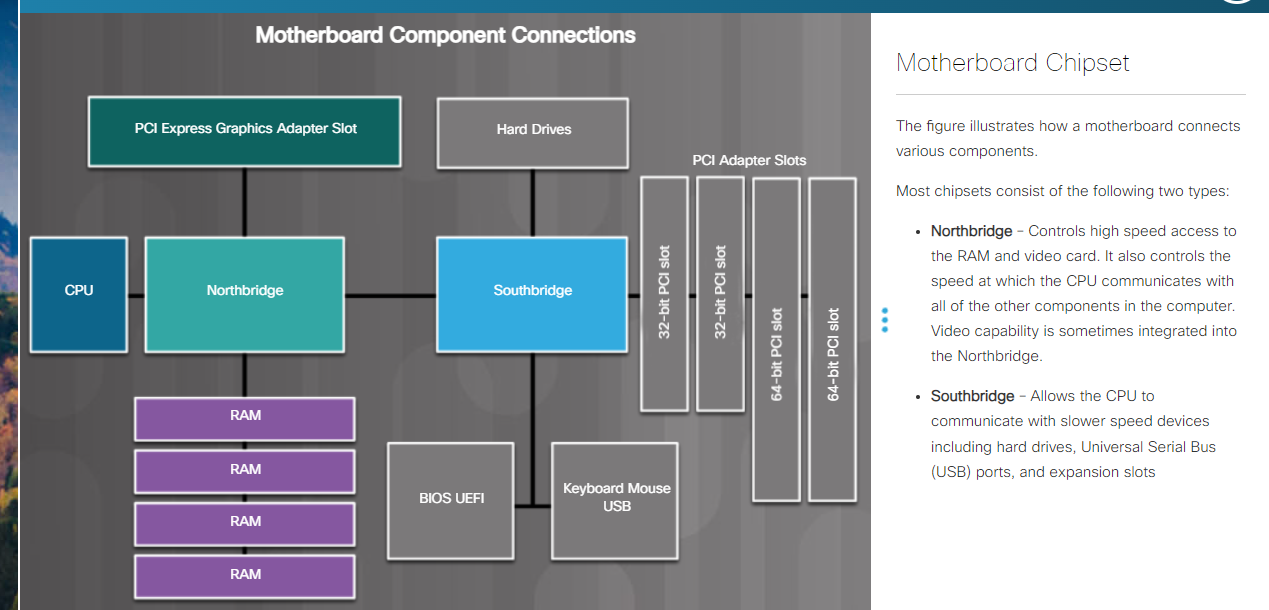
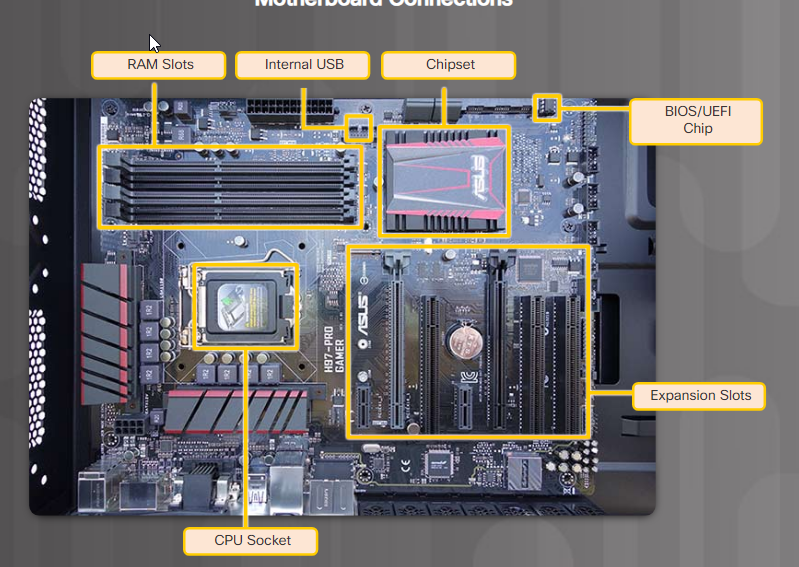
- Motherboard: The main printed circuit board that connects all other internal components.
- Chipset: A group of integrated circuits on the motherboard that manage communication between various components.
- Northbridge: Manages high-speed communication between CPU, RAM, and video card.
- Southbridge: Connects the CPU to slower devices like storage drives and USB ports.
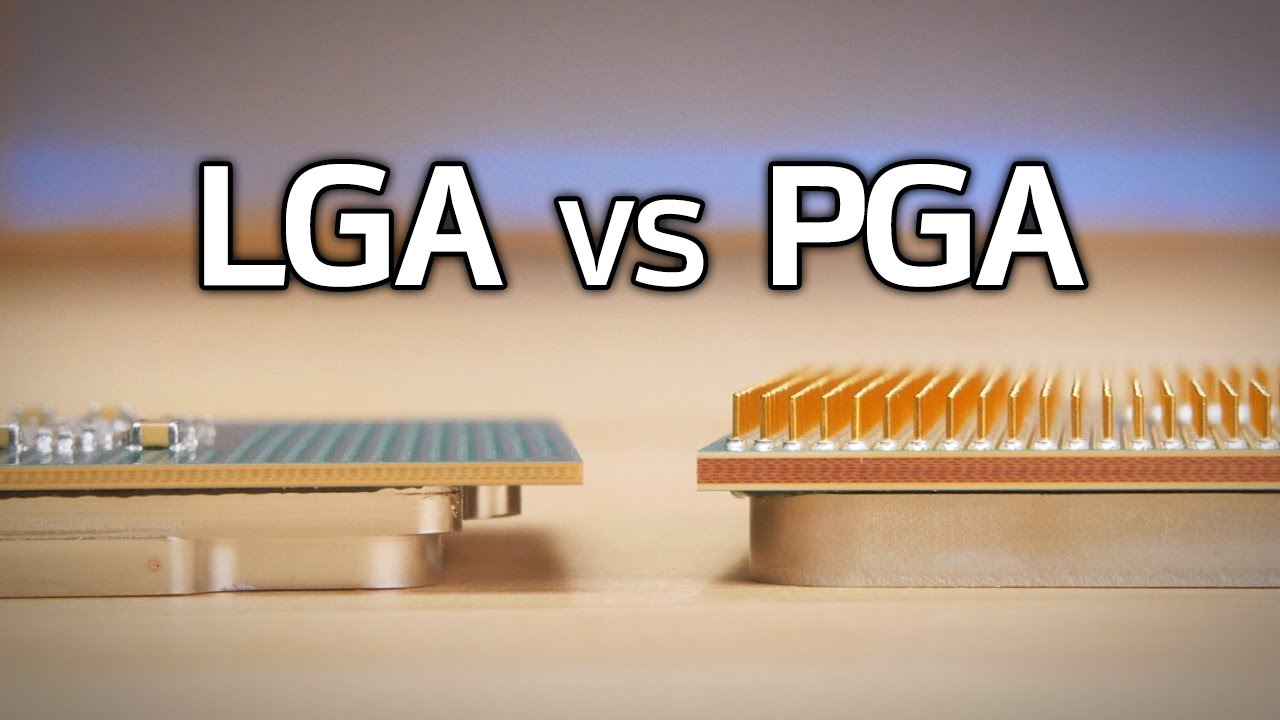
- CPU Socket: The physical slot where the CPU is installed. Socket type determines CPU compatibility.
- LGA (land grid array) is pins on socket
- PGA (pin grid array) pins on cpu
- Memory Slots: Slots for installing RAM modules. Number and type of slots depend on the motherboard.
- Expansion Slots: Provide connectivity for additional functionalities like graphics cards, network cards, and sound cards.
- Connectors: Provide connections for internal components like storage drives and front panel features (power button, USB ports, etc.).
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The brain of the computer, responsible for processing instructions and data.
- Cores and Threads: Modern CPUs have multiple cores (processing units) and threads (execution paths) for improved performance.
- Clock Speed: Measured in GHz and indicates the number of cycles the CPU can complete in one second. Higher clock speeds generally mean faster performance.
- Cache: High-speed memory built into the CPU for storing frequently accessed data.
- Heat Sink and Fan: Essential for dissipating heat generated by the CPU during operation.
- Memory (RAM): Volatile memory that stores data for temporary use by the CPU.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Allows data to be accessed from any location with equal speed.
- Memory Types: Common types include DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 (differ in speed and compatibility).
- Memory Capacity: Measured in Gigabytes (GB) and determines how much data the RAM can hold at once.
- Memory (Rom)
- EPROM (erasable with ultraviolet light), PROM,EEPROM (generally non erasable but can be flashed over (used for bios))
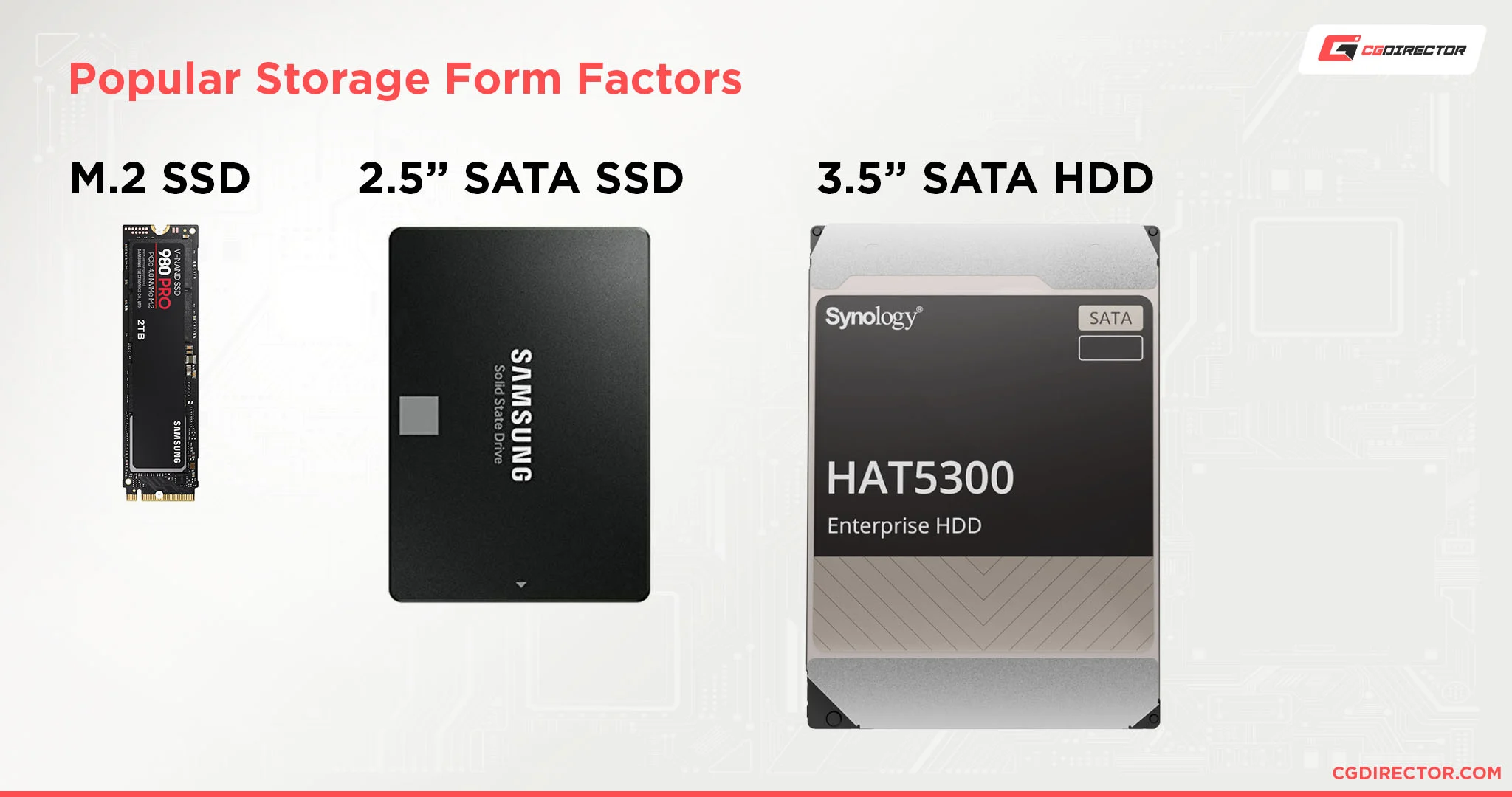
- Storage Drives: Used for long-term data storage.
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD): Uses a spinning disk and magnetic head to read and write data. Offers large storage capacities at a lower cost, but slower access times.
- Solid-State Drives (SSD): Uses flash memory to store data electronically. Provides faster access times, but typically lower capacities and higher cost per gigabyte.
- Storage Interfaces: Connect storage drives to the motherboard. Common interfaces include SATA and NVMe.
- Expansion Cards: Add additional functionality to the computer.
-
Graphics Cards (Video Cards): Enhance the computer’s graphics processing capabilities for gaming, video editing, etc.
-
Network Interface Cards (NICs): Provide network connectivity (wired or wireless).
-
Sound Cards: Enhance the computer’s audio capabilities.
-
Other Expansion Cards: FireWire cards, USB expansion cards, etc. (depending on build)
-
PICS
MOBO

Cables





STORAGE
PSU’s