Rounding
when at exactly .5 (not like .51) round to the even. so 2.5 > 2 & 3.5 > 4
Guess format (how to answer problems)
- Given: List the known information using appropriate symbols and numerical values, including units.
- Unknown: State the quantity or quantities you need to find.
- Equations: Identify the relevant equations or principles that relate the given and unknown quantities.
- Solve: Manipulate the equations algebraically and substitute the given values to solve for the unknown(s). Show all steps and calculations clearly.
- Sentence: Write a clear and concise sentence that answers the question posed in the problem, including the numerical value and correct units. Consider significant figures.
Example:
- Given: A car travels 150 kilometers in 2 hours.
- Unknown: Average speed of the car.
- Equations: speed = distance / time
- Solve: speed = 150 km / 2 h = 75 km/h
- Sentence: The average speed of the car is 75 kilometers per hour.
Significant Figures
- Nonzero Digits: Always significant.
- Ex: 211.8 has four significant figures.
- Zeros Between Nonzeros: Always significant.
- Ex: 20,007 has five significant figures.
- Leading Zeros: Never significant.
- Ex: 0.0085 has two significant figures.
- Trailing Zeros (Whole Number with Decimal): Always significant.
- Ex: 320. has three significant figures.
-
- Trailing Zeros (Whole Number without Decimal): Never significant.
- Ex: 32000 has two significant figures.
- Trailing Zeros (Whole Number without Decimal): Never significant.
- Trailing Zeros (Decimal Number): Always significant.
- Ex: 12.000 has five significant figures.
- Exact & Irrational Numbers: Infinite significant figures.
- Ex: 1 meter = 100 centimeters, e, π
- Scientific Notation: Only consider the coefficient (A) for significant figures.
- Ex:
- 4.5 × 10³ has two significant figures.
- 4.50 × 10³ has three significant figures.
- 4.500 × 10³ has four significant figures.
- Ex:
Calculating with Sig Figs
Multiplying/Dividing
When multiplying or dividing the answer is limited to the lower number of sig digits of the terms being multiplied or divided
Adding/Subtracting
When Adding and subtracting values, the answer is always rounded to the same number of digits to the right of the decimal point as that of the least precise quantity.
Electricity
Electric Current
Electric current (I):
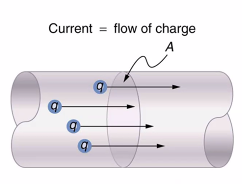
Measure of the rate of electron flow at a given point in a circuit, measured in amperes (A)
- I = Q/t, therefore 1A = 1C/s (… A = C/s)
A current of 1 ampere means electrons are flowing through there very second
Direct Current (DC)
The movement of electrons in only one direction
Alternating Current (AC)
The Movement of electrons in two directions
Ammeter
Electrical device that measures electric current (must connect in series)
Electric Potential Difference (Voltage)
Electric Potential Difference
The amount of electric potential energy associated with the charges
Electric Potential difference (V)
The change if electric potential energy associated with charges at two different points in a circuit
Q may be referred to as C
Voltmeter
an electric device that measures electric potential difference (must be connected in parallel)
Resistance
Work
What is the resistance of a toaster with a voltage of 120v and a current of 6.5A
Given V & A
Unknown R
Equasion =
Solve:What is the resistance of a car starter with 450A of current and 12V
Solve:
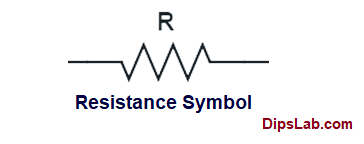
Electrical Resistance (R)
Ability of a material to oppose the flow of electric current; measured in ohms ()
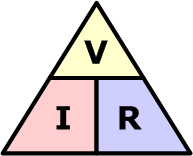
Ohms law
Factors that effect resistance
- type of material
- cross-sectional area
- How long*wide the material is
- length
- temperature
- hotter = more thermal energy
Resistors
A device that converts electrical energy to heat by reducing the flow of electric current
Kirchhoff’s law
Ohms Law
Units
Tips and Tricks
LEDS
- Long leg = Positive; Short = Negative
Definitions
Q
Q represents electric charge, it is used in Coulomb’s law
J
Joules
A format of energy (E)
In electronics, it’s the same amount of energy, in electrical units. One joule is one watt of power, applied for one second (a watt-second); or a coulomb of electrical charge raised to a potential of one volt.
Magnetism
Flows from North to South\
Lenz’s Law
If a changing magnetic field induces a current in a coil, the electric current is in such a direction that its own magnetic field opposes the change that produced it
Conversions
Kinematics
Equations
Scaler
Quantity that only has magnitude
Examples
Speed of 34km/h
4 hours
Vector
Quantity that has magnitude and direction
Examples
Velocity of 34km/h [E]
Displacement of 5km [S]
How to draw one
- Draw a line
- Draw a tip (arrow) pointing in the direction of choice
Adding/Sub
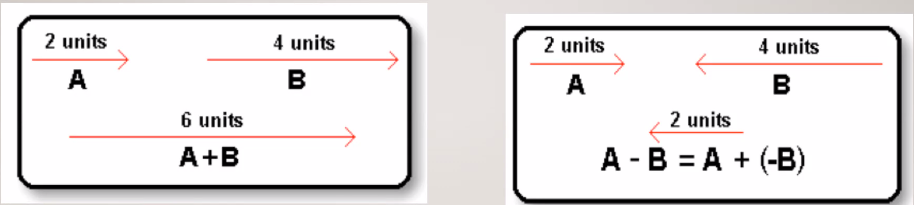
You quite literally add them up. if it’s negative, add the negative.
Displacement
the distance and direction of an object from a particular point in a straight line
e.g. The child was displaced 5km east
Tips
you must always have number, unit and direction
e.g. 5.2km [N]
Uniform vs Non-Uniform
Uniform - Speed is equal and in a straight line
Non-Uniform - Speed is non-equal or not in a straight line
Speed & Velocity
Average speed
() the total distance divided by total time taken
Average Velocity
the total displacement divided by the total time for that displacement
Acceleration
Acceleration () - rate of change of velocity divided by time
Positive: The direction of acceleration is the same as current velocity
Negative: It’s counteraction the current direction of motion (deceleration)
Gravity
Calculating complex displacements
Forces
Inertia
The ability of an object to resist change in motion
Once something is going, it doesn’t want to stop (and when it stopped it doesn’t want to start)
Mass vs weight
- Mass
- The amount of matter in an object
- Weight
- The amount gravitational attraction that is acting on an object
Common forces:
Net forces
The sum of all of the forces acting on an object.
5N of force to left, 10N to right. Net force: 5N right
Newtons (N)
Force of gravity
Measured in Newtons (N)
(mass (Kg) * )
Gravitational field strength
Fundamental forces
- Strong Nuclear
- Forces holding an atom together
- Weak Nuclear
- Between molecules (eg. h2o to h2o) or DNA’s helix shape
- Electromagnetic
- Caused by electric charges
- Gravitational
Newton’s Laws
Second Law
Energy & Work
- Energy: The ability to do work
- Work: The energy transferred to an object by a applied force over a measured distance
Formulas
W → Work (Joules)
F → Force applied (N)
→ displacement (m)
Work
Case 1: Positive work
Force applied and displacement are in the same direction
- E.g. lifting a bag
Case 2: Negative work
If force applied and displacement are in opposing directions
- E.g. a pully or a rocket running
Case 3: Work against gravity
If the force applied and displacement are both vertical and no acceleration occurs the work against gravity is positive
- E.g. an elevator
Case 4: Zero work
If force and displacement are perpendicular
Work Energy Princible
The net amount of mechanical work equals the object’s change in kinetic energy
Thermal Energy
Water Capacity
Homework
2024-07-05
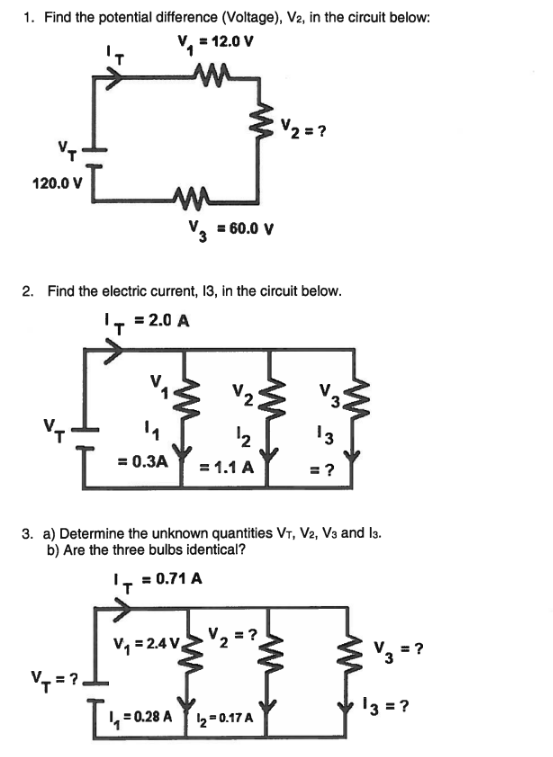

1
Since volts add up in series
2
Since Amps add up in a parallel circuit…
3
Since amps split and volts are the same, we can find that all V’s are
4
This one’s weird but it’s still parallel and it adds up;
5
This one is series so we need to find
6
Okay so we need to find a couple of Amp messurements
since the amps split where the wires split we can assume are both
has never split so it must be the same at so if we add it up
7
A)
Since we have all values.. we can just add them up
B)
This is also series so we know the voltage adds up, if the total if 9v we can just subtract the values we know, so..
2024-07-08
Simple Series And Parallel Circuits.pdf - Google Drive
1
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 6 | 0.2 | 30 |
| 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 0.2 | 25 |
2
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 50 | 7.5 | 6.7 |
| 1 | 50 | 4.2 | 12 |
| 2 | 50 | 3.3 | 15 |
3
Type: Series
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 6 | 5 | 1.2 |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 0.6 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 2 | 5 | 0.4 |
4
Type: Parallel
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 24 | 8.4 | 2.85 |
| 1 | 24 | 1.2 | 20 |
| 2 | 24 | 2.4 | 10 |
| 3 | 24 | 4.8 | 5 |
5
Type: Series
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 3 | 0.086 | 35 |
| 1 | 1.29 | 0.086 | 15 |
| 2 | 1.72 | 0.086 | 20 |
6
Type: Series
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 3 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 3 | 0.5 |
7
Type: Parallel
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 120 | 2.2 | 54.5 |
| 1 | 120 | 1 | 120 |
| 2 | 120 | 1.2 | 100 |
8
Type: Parallel
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 12 | 0.96 | 12.5 |
| 1 | 12 | 0.6 | 20 |
| 2 | 12 | 0.24 | 50 |
| 3 | 12 | 0.12 | 100 |
Extra hard question (Combo circuit) 🥰
Combination Circuit Example.pdf - Google Drive
| V | I | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 24 | 2 | 12 |
| 1 | 16 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 (parallel) | 8 | 2 | 4 |
2024-07-09

1
Use Conversions
2
Use Conversions #2
2024-07-11

1
use #2 from Equations
Given: initial (0 speed) time (15s) acceleration ()
Unknown: displacement
equation: #2
solve:
Sentence: The care was displaced m [N] away
2
Given: , and distance
Unknown: acceleration
equation: Acceleration formula
solve:
3
Todo: Figure out how to do this
Given: distance, acceleration
Unknown: time(s)
Equation: #2Solve:
Sentence:
2024-07-19
Friction
A 75 kg hockey player glides across the ice on his skates with steel blades. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.01. What is the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the skater.
Since the surface is horizontal
Force of friction

Forces 1
a)Therefor the string exerts a force of 0.60 Newtons on the string.
b) displacementTherefore the displacement of the cart is 8.4m [right]
c) Mechanical work… the mechanical work done is 5.0J

Yayyy

Kinetic energy
1
2
(note: convert grams to kg)
2024-07-24
Temp to mass
Given: Aluminium , energy absorbed
Unknown: Mass
Equation:
Solve:
Sentence: therefore the mass of the block is 2.2kg
Thermal Energy
FORMAT
Given:
Unknown:
Equation:
Solve:
Sentence:
WORk
###### Title
$$
\begin{align}
\end{align}
$$