🔁 Recursion in Java
What is Recursion?
Recursion is a programming technique where a method calls itself to solve a problem. It breaks down complex problems into simpler ones by solving smaller instances of the same problem
Key Components
- Base Case: The condition under which the recursion ends
- Recursive Case: The part where the method calls itself with a modified parameter
Example: Factorial Calculation
public class FactorialExample {
public static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0) { // Base case
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n - 1); // Recursive case
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(factorial(5)); // Outputs 120
}
}How It Works
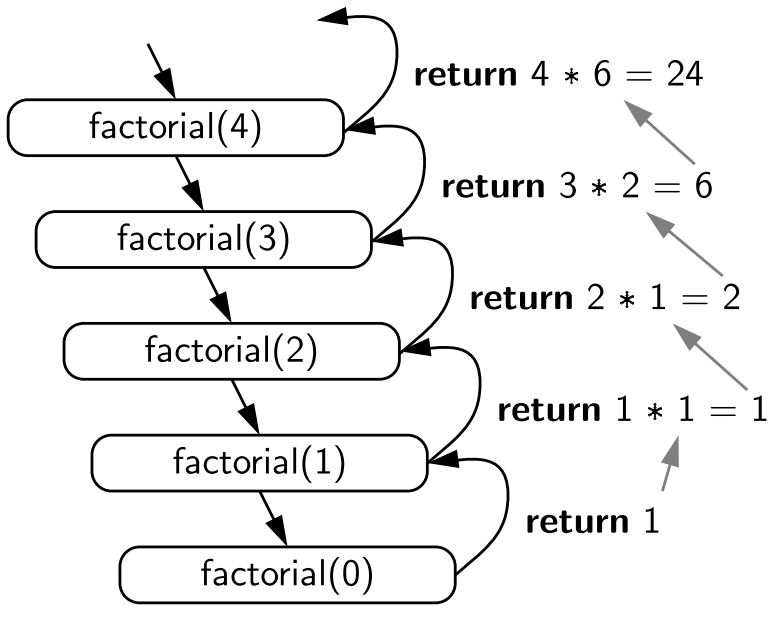
When factorial(5) is called, the method keeps calling itself with decremented values until it reaches the base case (factorial(0)), then the results are multiplied as the call stack unwinds
Visual Representation
A diagram showing the call stack for factorial(5)