🔍 Searching and Sorting in Java
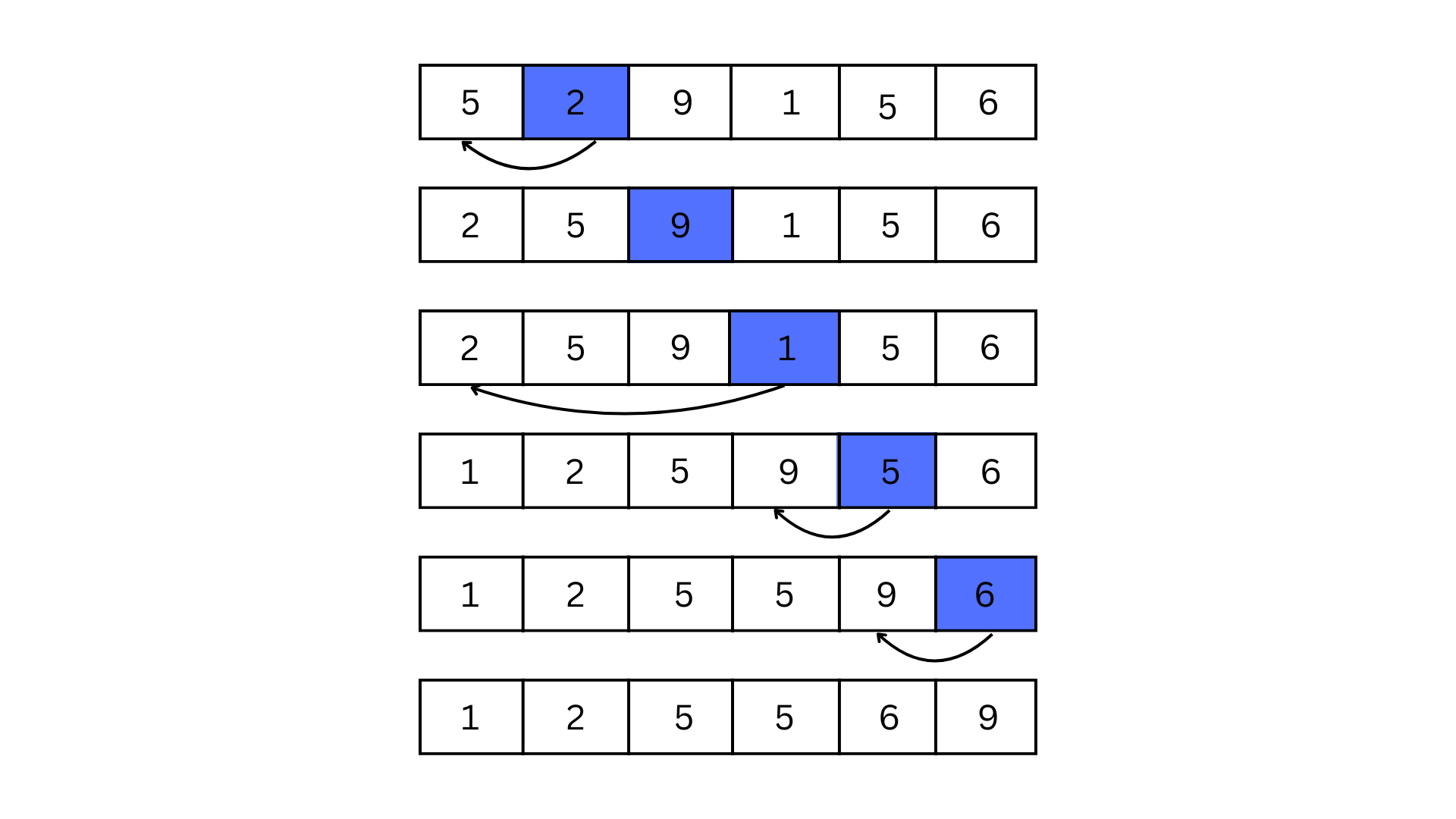
Searching Algorithms
Linear Search
Linear Search checks each element in the array until the desired value is found or the end is reach.
public class LinearSearchExample {
public static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i; // Target found
}
}
return -1; // Target not found
}
}- Time Complexity O(n)
Binary Search
Binary Search is efficient for sorted array. It repeatedly divides the search interval in half.
public class BinarySearchExample {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int low = 0;
int high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid; // Target found
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1; // Search right half
} else {
high = mid - 1; // Search left half
}
}
return -1; // Target not found
}
}- Time Complexity O(log n)
Sorting Algorithms
Selection Sort
Selection Sort repeatedly selects the minimum element and moves it to the sorted portion of the array.
public class SelectionSortExample {
public static void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
// Find the minimum element in unsorted array
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
// Swap the found minimum element with the first element
int temp = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
}- Time Complexity O(n^2)
Insertion Sort
Insertion Sort builds the sorted array one element at a time by comparing and inserting elements into their correct position.
public class InsertionSortExample {
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
// Move elements greater than key to one position ahead
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
}- Time Complexity O(n^2)
Understanding Big O Notation
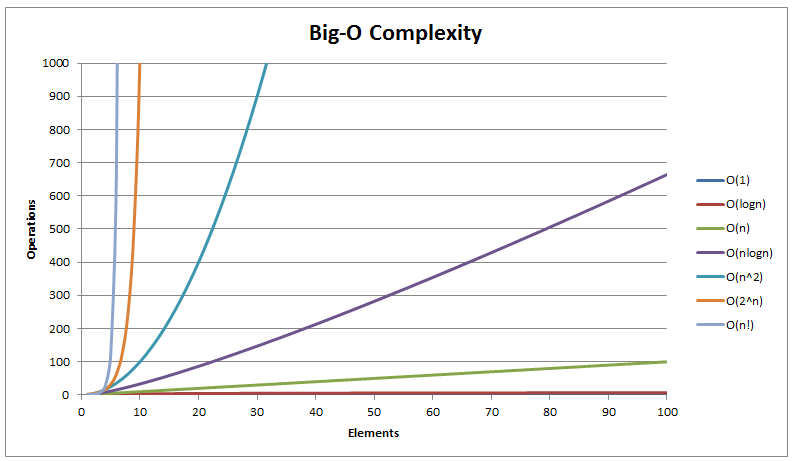
Big O Notation describes the upper bound of an algorithm’s running time as the input size grow.
-
O(1) Constant time
-
O(log n) Logarithmic time (e.g., Binary Search)
-
O(n) Linear time (e.g., Linear Search)
-
O(n²) Quadratic time (e.g., Selection Sort, Insertion Sort)
Further Learning
- Java Sorting Algorithms: A Beginner’s Guide - Medium
- Java Search Algorithms: Beginner’s Guide - Medium
- Java: Algorithms: Searching and Sorting Cheatsheet - Codecademy